1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
|
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import xlwt
import argparse
import sys
if sys.version_info.major < 3:
print("I need python3.x")
def parsexml(xml,sheet):
tree = ET.parse(xml)
root = tree.getroot()
hosts = root.findall("host")
i = 0
for host in hosts:
i += 1
portTcpRes = ""
portOtherRes = ""
ip = host.find("address")
ipaddress = ip.attrib.get('addr')
ports = host.find("ports").findall("port")
os = host.find("os")
try:
osmatch = os.find("osmatch")
osname = osmatch.attrib.get("name")
accuracy = osmatch.attrib.get("accuracy")
except Exception as e:
osname = ""
accuracy = ""
for portT in list(ports):
service = portT.find("service")
protocol = portT.attrib.get('protocol')
serviceName = service.attrib.get('name')
product = service.attrib.get('product')
if product:
serviceName = serviceName + ':' + product
portNum = portT.attrib.get('portid')
if protocol == 'tcp':
portTcpRes += portNum + '(' + serviceName + '),'
else:
portOtherRes += portNum + '(' + serviceName + '),'
output(sheet,ipaddress,portTcpRes.strip(','),portOtherRes.strip(','),i,osname,accuracy+"%")
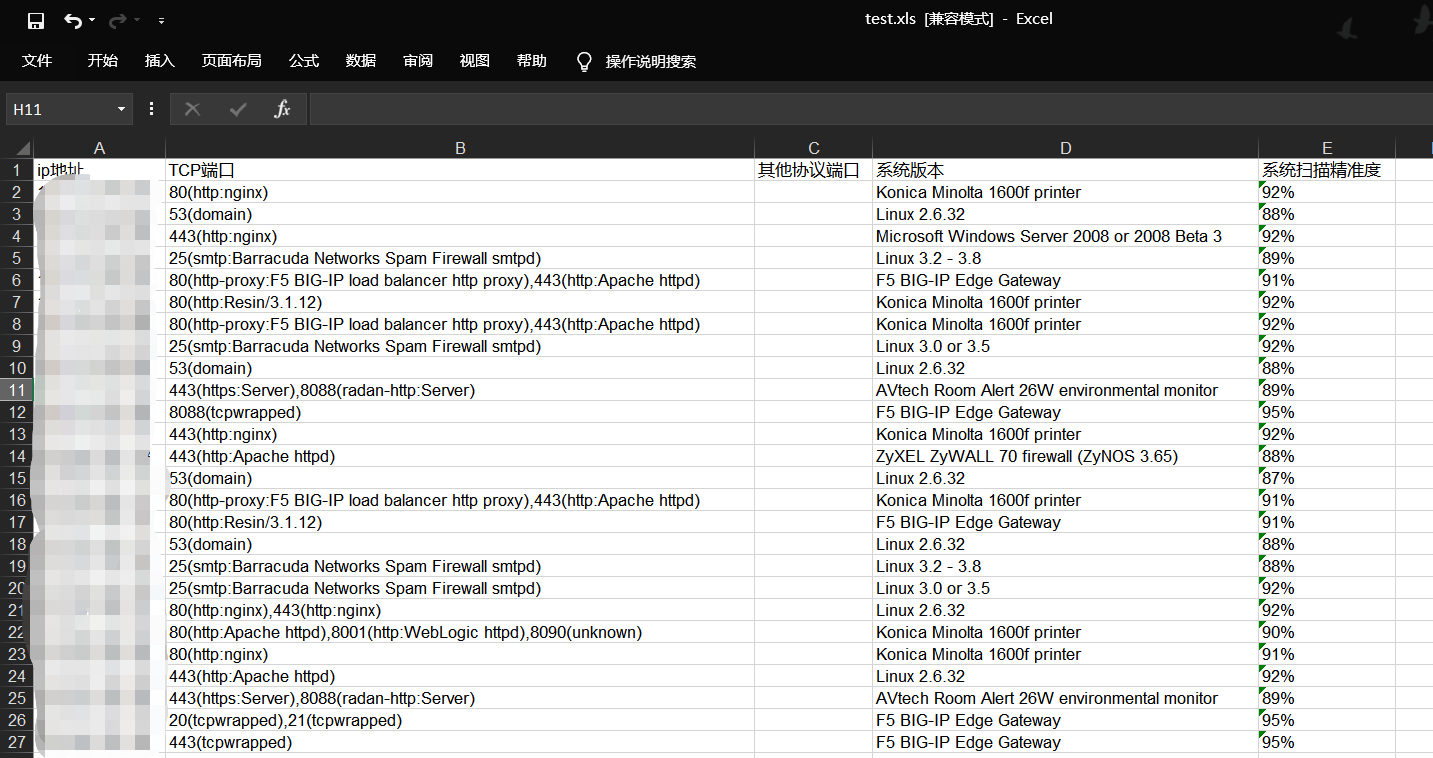
def excelcsh():
ExcelFile = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8',style_compression=0)
sheet1 = ExcelFile.add_sheet('nmap结果')
sheet1.write(0,0,'ip地址')
sheet1.write(0,1,'TCP端口')
sheet1.write(0,2,'其他协议端口')
sheet1.write(0,3,'系统版本')
sheet1.write(0,4,'系统扫描精准度')
return ExcelFile,sheet1
def output(sheet,ip,tcpport,otherproto,num,osversion,accuracy):
sheet.write(num,0,ip)
sheet.write(num,1,tcpport)
sheet.write(num,2,otherproto)
sheet.write(num,3,osversion)
sheet.write(num,4,accuracy)
sheet.flush_row_data()
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="xml解析")
parser.add_argument('-x',action="store",required=False,dest="xml",type=str,help='nmap result(xml file)')
parser.add_argument('-o',action="store",required=False,dest="outfile",type=str,help='outputName',default="excel.xls")
args = parser.parse_args()
xml = args.xml
outpath = args.outfile
if xml:
excelfile,sheet = excelcsh()
try:
parsexml(xml,sheet)
except FileExistsError as e:
print("xml文件不存在")
print(e)
excelfile.save(outpath)
print("文件保存至 %s" % outpath)
else:
print('Error args')
print('eg: python3 pythonXml.py -x nmap.xml -o nmap.xls')
|